This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Website Applications: Complete Guide
- 1: Application Types: Diffrent classes of websites for difference uses
- 2: Analytics: A guide from starter to hero
- 3: Applications: a guide on the many possibilities
- 4: Attribution: A Comprehensive Guide
- 5: Contact page: Exploring the best contact methods
- 6: Messaging: Using Applications and Data Pipelines
- 7: Tools: A guide on handy website features
- 8: Calendar: How to Use a Calendar with Your Website
- 9: Structure: Methods of custom analysis
- 10: QR Codes: Enhancing User Experience and Accessibility
- 11: Leveraging Digital Business Cards (vCards) for Success
- 12: Doc Signing: Make E-Signing Simple, Secure, and Free
- 13: Payment: A Smarter Way to Handle Payments
- 14: Digital Signage: Using the Web as a Display Engine
1 - Application Types: Diffrent classes of websites for difference uses
Many online tools offer features catering to a use case, and these applications may operate with different modes. It’s not immediately obvious which is which, and harder still to disambiguate them when attempting to search any results. Some common and long-standing ways have become common. To list a few:
- n online - To find an online variant of a tool
- n desktop application - to find a desktop application to download
- n MacOs App
- n Android app
- …
However, these terms are becoming more dated as things evolve, with new technologies becoming available and more standardised ways of doing business are becoming evident.
Website Types
Important command types that are available to websites are as follows.
- Online web-to-server
- Online web-to-local context
- Online web to local filesystem
- Online web-to-tunnel
Each of these types offers different functionality and restrictions, and not all websites can offer all modes. The best type of application for a website is to offer all the available types. Since each type has its advantages and disadvantages, it can be good to let the user choose.
To illustrate the difference between a web-to-server and a web-to-local context type and show how it’s good to offer both types when possible. Let’s look at the process of compressing an image. It’s a task that I do just enough to care about and not enough to keep a full-fledged editor software on my computer. So I often find myself looking for an application to perform the conversion. While there are undoubtedly ways to perform such an operation using the features available on my operating system. I simply want a smaller image, so I Google for PNG compressor, I upload the file, and there you go, a smaller image. Hurrah, magic.
This method is great until you realise that you have just uploaded that picture to a server owned by a random developer. This can also be a problem when dealing with sensitive inventory or other legal requirements.
Web-to-server
With web-to-server the image is uploaded to a server, often just for the compressing of the image, but perhaps for other more malicious purposes. Instances of unwanted leaks have become commonplace in the world of generative AI prompts, with users uploading sensitive information without understanding that the terms of operating mean that any information may be used as training data. Which can cause the data to be repeated within the public domain. However, with web-to-server, it can also offer major improvements in all areas. For example, well-designed and operated websites offer service-level agreements that provide military-grade redundancy and much more.
Web-to-local context
With web-to-local context, the image compression is done in the browser sandbox. This means that the data (the image) is never transmitted to the origin domain(website). So there can be no leaks? Great, that sounds better. But it’s not all smooth sailing. Just like any website you are still using someone’s property, so it’s important to be aware of the terms of the service. In addition, using only the local context within a web browser can be much slower than using an industrial server, and runs on the electricity and computational limits of the machine executing it.
Web-to-local
Web-to-local application run on WASM and JavaScript engines within the browser to execute code, and utilise the Web Storage API to store data for next session locally.
The term local can mean multiple things:
- Persistant - Storing within the filesystem of the device, meaning it access the operating systems filesystem like an applicaiton (with added permissions and restrictions).
- Context - Storing within a context limited origin of the website, meaning only that website and its code can access the file storage objects.
- Temporary - Storing within only the current browsing session of an origin.
- Page - Storing any data only for each page request.
### Context
Web-to-local content type websites save their data using the Web Storage API, which means the data is stored locally in the browser’s storage. This storage is subject not only to the origin’s storage sandbox but also to the broader control of the browser. As a result, if a user clears their browser data—such as when deleting browser history—it will also wipe out any stored data associated with the web application, even if the application itself wasn’t accessed during the process. This means that important data can be lost without any interaction with the web app. Therefore, it’s essential to regularly export any files or data you are working on to ensure they are not inadvertently erased.
Conclusion
Since it can be hard to tell a type from looking at an applicaiton, you must check the applications documentation.
2 - Analytics: A guide from starter to hero
What is analytics, and how does it work?
Analytics is an essential tool that every website owner should use to monitor their website’s performance. With analytics, website owners can measure the effectiveness of their online campaigns and understand how their audience interacts with their website. Analytics features provide an in-depth view of website traffic, user behavior, and demographics, which can help you make informed decisions about your website’s content and design.
One of the significant benefits of analytics, which monitors website interactions, is that it offers insights into how website traffic flows. With analytics, website owners can track the number of visitors to their website, where they come from, and how long they stay on the site. This information is critical in determining how well your website is performing and identifying areas where you can improve.
Analytics features can also help you identify your website’s most popular pages and the content that resonates best with your audience. This data can help you create more relevant and engaging content, which can attract more visitors to your website. In addition, analytics can show you which pages are not performing well, giving you an opportunity to make improvements and increase engagement.
Another significant benefit of analytics features is that they can help you understand your audience better. With analytics, you can track user behavior, such as which pages they visit most frequently, how long they stay on each page, and what actions they take on your website. This data can help you create a more personalized experience for your visitors, which can improve engagement and increase conversions.
Analytics features can also help you identify trends in user behavior, such as the devices and browsers your visitors use. This information can help you optimize your website for different devices and increase accessibility for all visitors.
Google Analytics vs. Custom Server or Code Tracking
Google Analytics is a web analytics service by Google, providing features to track and analyse website traffic. It offers pre-built reports and dashboards for insights without extensive customization. However, users can extend custom reports in various ways, subject to account limitations. On the other hand, custom server or code tracking allows for highly tailored data points. However, it’s important to note that using custom server code requires rewriting many components that established analytics software already includes. This makes it a costly implementation unless you have a critical need for highly specific and tailored data points. Google Analytics integrates with other Google services for seamless online marketing tracking. The choice between the two depends on specific needs and technical capabilities, each offering distinct advantages for tracking and analysing website activity.
How Businesses Can Effectively Use Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a powerful tool for businesses looking to improve their website’s performance and get a better understanding of their tra. In this article, we’ll discuss various ways businesses can use Google Analytics to monitor website trends, understand usability patterns, create better content, and more.
Monitoring website trends
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that businesses can use to track website traffic and gain insights into user behavior. By analysing this data, businesses can make informed decisions about their website’s design, content, and marketing strategies. Implementing Google Analytics is straightforward for many websites, often requiring only the addition of analytics scripts to begin gathering valuable information. While the default options are effective, businesses can also customise metrics and dimensions to capture specific data relevant to their goals. Some key metrics that businesses should monitor include:
- Traffic sources: Google Analytics can show where visitors are coming from, such as search engines, social media, or referral sites. This information can help businesses determine which channels are driving the most traffic to their site.
- Pageviews: Tracking pageviews can help businesses identify the most popular pages on their site, as well as pages that may need improvement.
- Bounce rate: The bounce rate shows the percentage of visitors who leave a site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate may indicate that visitors are not finding what they are looking for on the site.
- Time on site: Tracking the amount of time visitors spend on a site can help businesses determine how engaging their content is.
- The crawl path: How do the users navigate your website, starting on a home page and moving to the context page? Are they skipping your calls to action or FAQs before calling you?
- Number of users: Depending on how your analytics are configured, you may collect the session information of customers over long periods of time while within your website. However, more strict analytics configurations track a user’s session for only 24 hours before creating a new one. Having a low tracking period can cause your analytics data to seem less accurate because it tracks the same users multiple times if they return to the same website. But this is expected; in this case, the meaning of user now does not mean a person or device, but instead a unique device session for 24 hours.
- What is NOT captured: Your website analytics do not collect all available data. For example, answer engine widgets may provide information to users without your website being able to collect any data. The impressions and engagements for the respective applets may be displayed within their own user interface. For example, with Google Business, simply Google your business while logged into your Google account to see an administration panel. To conduct a full analysis, it is best to accumulate data from many sources. For example, a user may see your business on a search engine and not perform a call to action like a phone call or website click. Even after being prompted with a rich result displaying your calls to action, this would be captured by a Google Business impression without an engagement. As your Google Business applet result displays only a summary of your information, a follow-up to an answer engine prompt by using a call to action would be a request for more information. It’s also worth noting that answer engines are becoming more capable of answering inquiries without any further call to action.
By monitoring these metrics, businesses can make data-driven decisions about their website’s design and content.
Utilizing Analytics Notifications for Improved Website Insights
Analytics services like Google Analytics offer powerful notification features that help businesses stay informed about key performance metrics. These services can be set up to monitor a range of insights, such as user behavior, traffic sources, or conversion rates, and provide notifications based on selected metrics. This capability allows business owners to stay updated without having to constantly check their dashboards.
For example, in Google Analytics, the notifications can be configured within the Insights panel. This allows users to choose specific insights they wish to receive alerts for, such as daily user counts, new traffic spikes, or goal completions. To set this up, simply navigate to the Insights panel, select the insight that aligns with your business goals, and enable notifications.
This functionality is particularly useful for businesses aiming to stay proactive about their website’s performance. By receiving real-time alerts, they can quickly identify trends, address any issues, or capitalize on opportunities as they arise. It enables businesses to maintain a closer connection to their online audience and make data-driven decisions promptly.
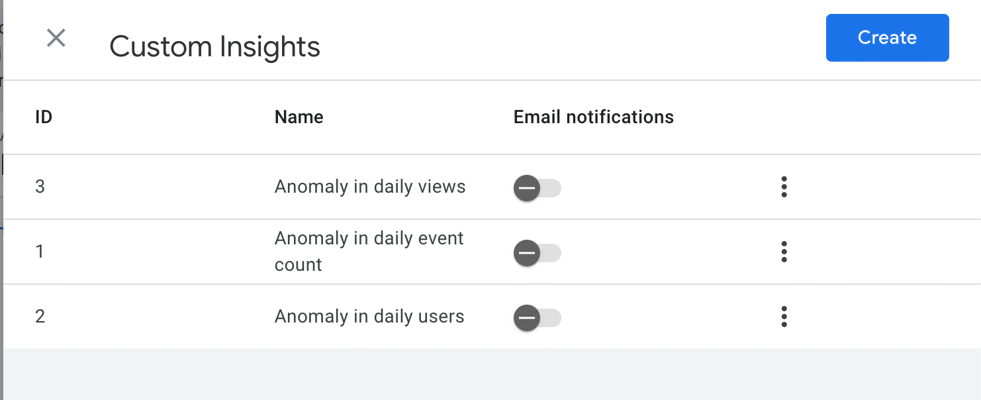
One-click insight notification options in Google Analytics > Insights
Analytics tools like Google Analytics offer flexibility in configuring notifications for both existing and custom data metrics. Users can set up notifications for predefined metrics, such as user sessions, bounce rates, or goal completions, as well as custom metrics tailored to their unique business needs. These insights can be configured to push alerts directly to your devices whenever a new report or significant data update becomes available. This ensures that you’re immediately informed of any changes or trends, allowing you to respond quickly to new information and make informed decisions based on the most up-to-date analytics.
Recording Custom Data Events
Google Analytics allows businesses to track custom data events, such as button clicks, downloads, and form submissions. This information can help businesses better understand how users interact with their site. For example, tracking how many users click on a specific button can help businesses determine whether the button is effective in driving conversions.
To track custom data events, businesses can use Google Tag Manager, which allows them to add code snippets to their site without needing to modify the site’s source code. This makes it easy for businesses to track user behavior without needing to involve their development team.
You can find more information on Custom events within Google Analytics here. For example, when using custom events within Google Analytics reports, to register event parameters and display them within your dashboard, you must first register the event parameter as a custom report dimension (subject to account limits). You may find the following article helpful: [GA4] About custom dimensions and metrics, and then, to create a report, see [GA4] Overview of Google Analytics reports and [GA4] Create an overview report. Once your report has been created you must publish it to the users with access to your Google analytics property. First create a collection, which is a set of reports, see [GA4] Collection. Once saved you can mark the collection as published and it will be avaliable within as a report on the Google Analytics Website.
Understanding Usability Patterns
Google Analytics can help businesses identify usability issues on their website. For example, businesses can use the Site Search feature to see what users are searching for on their site. If users are frequently searching for a specific product or service, businesses can make sure that information is prominently featured on their site.
Another way Google Analytics can help businesses understand usability patterns is by tracking user flows. User flows show the path users take through a website, from the entry point to the exit point. By analyzing user flows, businesses can identify pages that are causing users to leave the site, as well as pages that are leading to conversions.
Improving Existing Content
Google Analytics can help businesses identify which pages on their site may need improvement. For example, businesses can use the Behavior Flow report to see which pages users are exiting from most frequently. If users frequently leave a page without completing an action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form, businesses may need to revise the page’s design or content. Integrate with methods of A-B testing to get concrete insights on the most valuable changes you are unsure of.
Additionally, analytics provides vital data for various other applications. Typically, the most important are search reports.
Creating better content
Google Analytics can also help businesses create better content. By analyzing which pages on their site are the most popular, businesses can identify topics that their audience is interested in. They can then create more content on those topics to attract additional traffic to their site.
Additionally, businesses can use Google Analytics to monitor the success of their content marketing efforts. For example, by tracking how many leads or sales a piece of content generates, businesses can determine which types of content are most effective in driving conversions.
Understanding the Success of Advertising Campaigns
Google Analytics can help businesses monitor the success of their advertising campaigns. For example, businesses can use the Campaigns feature to track how many visitors are coming to their site from specific advertising channels, such as Google Ads or social media ads.
Additionally, businesses can use the Multi-Channel Funnels report to see how different advertising channels are contributing to conversions. This information can help businesses determine which channels are most effective in driving conversions and adjust their advertising strategies accordingly.
Monitoring advertising campaigns
In addition to monitoring the success of advertising campaigns, Google Analytics can also help businesses monitor their advertising spend. For example, businesses can use the cost analysis report to see how much they are spending on each advertising channel and determine whether their advertising budget is being used effectively.
Monitoring the social referral graph
Google Analytics can help businesses track how their content is being shared on social media. For example, businesses can use the referral report to see how many visitors are coming to their site from specific social media channels, such as Facebook or Twitter.
Understanding Users
Finally, Google Analytics can help businesses understand their audience better. For example, businesses can use the Demographics and Interests reports to see data on their audience’s age, gender, and interests. This information can help businesses create content that is tailored to their audience’s preferences.
Maximizing Marketing Impact with Data Analytics: Strategies and Insights
Data analytics is a critical tool for modern marketers to understand their audience and improve their marketing strategies. However, once you have set up your analytics solution, it’s essential to know how to get insights from it. In this article, we will discuss various strategies and insights to maximize your marketing impact.
Understanding the sources of your website
Understanding where your website traffic is coming from is critical to creating an effective marketing strategy. By analyzing your traffic sources, you can determine which channels are driving the most traffic to your website. You can then focus your efforts on these channels to maximize your marketing impact. You can use tools like Google Analytics to analyze your website traffic sources and get insights into how users are finding your site.
Targeting the correct sources
Once you have identified your website traffic sources, the next step is to target the correct sources. You can use data analytics to determine which channels are driving the most conversions and focus your efforts on these channels. For example, if you find that most of your conversions come from organic search, you can optimize your SEO strategy to improve your search rankings.
Understanding your users and their demographics
Knowing your audience’s demographic information is essential to creating an effective marketing strategy. By understanding your audience’s age, gender, location, and interests, you can create targeted campaigns that resonate with them. You can use tools like Google Analytics to get insights into your audience’s demographics and tailor your marketing efforts accordingly.
Understanding users’ behavior
Understanding how users behave on your website is critical to creating an effective marketing strategy. By analyzing user behavior, you can determine which pages are driving the most engagement and optimize them for conversions. You can use tools like heat maps and session replays to get insights into user behavior and improve your website’s user experience.
Optimizing your users’ flow through to the sale
Once users are on your website, it’s essential to optimize their flow through to the sale. By analyzing your website’s user flow, you can determine which pages are causing users to drop off and optimize them for conversions. You can use tools like A/B testing to experiment with different designs and messaging to improve your conversion rate.
Understanding what you can get from your analytics solution
It’s essential to understand what you can get from your analytics solution to maximize its potential. While graphs and tools provide valuable insights into your audience and marketing campaigns, they can only take you so far. You need to understand the limitations of your analytics solution and supplement it with custom tags and data points.
Adding custom tags and data points
Adding custom tags and data points to your analytics solution gives you the ability to write custom queries and get more insights into your audience and marketing campaigns. You can use languages like BigQuery to process large data sets and produce charts and other data points that can help you make informed marketing decisions.
Ensuring all your sources and campaigns are correctly attributable?
Attribution is critical to understanding the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns. With the demise of third-party cookies, it’s essential to ensure that all your sources and campaigns are correctly attributable. You can use tools like Google Tag Manager to track user behavior and ensure that all your sources and campaigns are correctly attributed.
Define what information you want to collect, identify what conversions you expect from any given campaign, and determine which report type to collect. The final output is one or both of the two report types: event-level reports and summary reports.
How to Restrict Analytics Usage for Internal Website Users
Ensuring that internal website visits, such as those made by administrators or internal staff, are excluded from analytics is crucial for maintaining accurate and actionable data. Internal users often visit every page during testing or maintenance, and counting these visits can distort metrics, making it appear that pages are more popular or visited than they actually are by external users. By filtering out this internal traffic, businesses can achieve a clearer picture of user behavior and interactions on their website. Here are a few methods to prevent internal traffic from skewing your analytics data:
1. Block Analytics Requests in the Browser
If you know the analytics software, you can use a plugin supported by its creator. For example with Google analytics, on supported browsers you can use the Google Analytics Opt-out Add-on (by Google).
One straightforward way to prevent internal users’ visits from being tracked is to block the analytics software’s requests directly in their web browsers. This method is relatively simple and requires no changes to the analytics software’s configuration:
- Using Developer Tools:
- Navigate to the page you want to exclude from tracking.
- Open the Developer Tools in your browser (usually accessible through F12 or right-clicking and selecting “Inspect”).
- Go to the Network tab.
- Identify the requests made to the analytics service, such as <www.googletagmanager.com> or region1.google-analytics.com.
- Right-click the request and select Block request domain or a similar option.
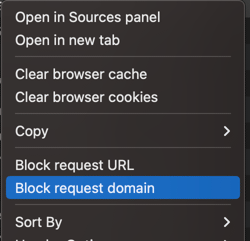
Option to block requests in the browser.
This method ensures that the browser will not send any tracking data to the analytics service, effectively removing those visits from being counted. However, it needs to be set up for each browser individually, making it less practical for larger teams. Remember to make sure the Enable network request blocking option is also enabled, otherwise your settings won’t work.
2. Filter IP Addresses in Analytics Software
Another method, and often a more robust one, is to use the IP filtering options within your analytics software:
- Set Up an IP Address Filter: Most analytics tools allow you to exclude traffic coming from specific IP addresses or IP ranges. This is particularly useful for blocking all traffic coming from within your office or organization’s network.
- Determine the IP address range that your internal users operate within.
- Configure the analytics software to exclude these IP ranges. This process is usually found in the settings under filters or data collection exclusions.
You can read more on Google Analytics Data Filtering - here.
By doing this, any requests coming from the specified IP range will not be counted, ensuring that internal traffic doesn’t mix with data from actual users. This approach is more centralized, ensuring that no visits from designated IPs are ever logged, regardless of individual browser settings. It’s particularly useful if your team uses a consistent office network or a VPN that ensures everyone appears under the same IP address.
3. Use a VPN with a Specific IP for Internal Users
If your internal users are often remote or work from varying locations, using a VPN service can help centralize their IP address:
Require VPN for Internal Users: Have internal users connect to a VPN that assigns them a consistent IP address when working on the website. Exclude VPN IP in Analytics: Set up a filter in your analytics software to exclude traffic from the VPN’s IP address. This method ensures that all internal users, regardless of their physical location, are recognized by the same IP address, making it easier to exclude their visits. This approach can be slightly more complex to implement but offers a robust solution for remote teams.
By implementing these methods, businesses can ensure that their analytics data remains accurate and reflects the behavior of actual users, free from internal testing or browsing activities. This leads to more reliable insights, enabling better decision-making based on user engagement and performance.
Custom event templates
Page helpful event
By adding a simple button to your website, such as the one below, you can create a powerful tool for gathering feedback to improve your content. While there are other methods for collecting feedback, such as user surveys or AI chat agents, an unobtrusive button allows for unbiased feedback without requiring the user to exert any effort.
In addition to gathering simple feedback, a feedback button can also prompt users to provide additional information or participate in a supplementary survey. This added functionality allows you to gather more detailed insights and opinions from your users, enabling you to make more informed decisions and improvements to your website or content. By leveraging the feedback button for supplementary interactions, you can enhance the depth of feedback and engagement with your audience, leading to a better understanding of their needs and preferences.
Info:
How is this data useful?
When you have a lot of documentation, and not enough time to update it all, you can use the “was this page helpful?” feedback data to help you decide which pages to prioritize. In general, start with the pages with a lot of pageviews and low ratings. “Low ratings” in this context means the pages where users are clicking No — the page wasn’t helpful — more often than Yes — the page was helpful. You can also study your highly-rated pages to develop hypotheses around why your users find them helpful.
In general, you can develop more certainty around what patterns your users find helpful or unhelpful if you introduce isolated changes in your documentation whenever possible. For example, suppose that you find a tutorial that no longer matches the product. You update the instructions, check back in a month, and the score has improved. You now have a correlation between up-to-date instructions and higher ratings. Or, suppose you study your highly-rated pages and discover that they all start with code samples. You find 10 other pages with their code samples at the bottom, move the samples to the top, and discover that each page’s score has improved. Since this was the only change you introduced on each page, it’s more reasonable to believe that your users find code samples at the top of pages helpful. The scientific method, applied to technical writing, in other words!
Excerpt from: docsy.dev.
Frequently asked questions
See our guide to attribution for more information.
Does Google Analytics (G4A) use cookies?
As of 2024 G4A does use first party cookies. This means google can track users across your domain using an identifier which they control the expiry date of. Since 2019 the default setting has been to only use first party cookies.
Does Google Analytics 4 (GA4) support the Privacy Sandbox?
Yes, Google Analytics cookies are first-party cookies, which means they can operate after the implementation of the so-called cookie-less advertising technology. Check out their notice here.
Are Google Analytics server-side events better?
They can be. For example, to ensure event integrity, or with regards to the privacy sandbox, it allows operating without third-party cookies. However, this analytics solution hides the analytics scripts behind the first party to prevent sending PPI to third parties via user TCP requests. Since 2019, web browsers have defaulted to using first-party cookies. However, enabling server-side events does give you access to more data within the Google Analytics ecosystem. This may be a major benefit only for small use cases. The extra data that is captured are events that did not originate from a browser window. On top of the negatives, client-side events must be configured by a developer, and that comes with implementation and utility costs. Since the events coming from users using a browser window are the important ones, it often makes no sense to incur any cost for data about robots using your website. You already have server logs. It can also help reduce client-side loading times by simply not serving a whole analytics distribution. Another reason may be to track access to resources that don’t have a browser window to execute any analytics software.
What are Google Analytics server-side events?
It is tracking your users using a first-party proxy and sending only the required data to any third-party trackers. In this case, Google Analytics.
Who is Google Analytics Server Side Events For?
Large businesses that are already incurring many of the costs, or someone who wants reports on the robots browsing their website.
App recommendations
- Detailed information on website visitors - Google Analytics
- An advanced analytics tool - Google Tag Manager
- Microsoft search information - Bing Search Web Masters
- Google search information - Google Search Web Masters
- What is a search impression?
Conclusion
In conclusion, analytics features are a must-have for any website owner who wants to understand their audience better and improve their website’s performance. With analytics, you can gain insights into website traffic, user behavior, and demographics, which can help you make informed decisions about your website’s content and design. By leveraging the power of analytics, you can create a more engaging and personalized experience for your visitors, which can lead to increased engagement, conversions, and revenue.
By following these strategies and insights, you can maximize your marketing impact with data analytics. Understanding your audience, optimizing your website, and tracking your campaigns’ effectiveness are just a few of the many ways that data analytics can help you improve your marketing strategy.
3 - Applications: a guide on the many possibilities
Custom applications are designed to meet your unique business requirements. This means that you can create applications that do exactly what you need them to do. For example, you can create an application that allows your customers to book appointments, purchase products, or submit support requests. By creating custom applications, you can streamline your business processes and improve the customer experience.
Custom applications can also provide you with valuable insights into your business. For example, you can track customer behavior and preferences, which can help you make informed decisions about your products and services. You can also track sales data, which can help you identify trends and opportunities for growth. By leveraging the insights provided by custom applications, you can optimize your business processes and improve your overall performance.
Creating custom applications may seem like a daunting task, but it doesn’t have to be. There are many tools and platforms available that make application development accessible to non-technical users. For example, low-code platforms allow you to create custom applications without writing any code. These platforms provide drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built components, making it easy to create applications quickly and easily.
You don’t have to stand alone, many business provide services to support your application. Just how they would as a widget on a web page, a service can be invoked from any application. Using pre-built components and services is an excellent way to quickly integrate powerful functionality into your projects. Often, these solutions are freely available, allowing you to simply copy and paste them into your codebase. This approach enables you to focus on what truly matters for your project, saving time and effort while maintaining high-quality standards.
The type and scope of a component can vary greatly, from using a simple web component to enrich a website to integrating a fully-featured software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform. These components include everything from UI libraries and frameworks (like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS) to backend services (such as Firebase or Auth0 for authentication). Many of them are freely available or offer free tiers, making them especially valuable for smaller projects or startups looking to minimize costs while still delivering a professional product. This approach also simplifies the integration of best practices and industry standards, as these components are often created by experts in the field.
The number of these services are far too numerous to list, just google whatever you desire. For example: printing cards API. Another option may be. Example: printing SaaS.
- https://mailchimp.com - Automate your email marketing.
- FormSubmit - Creating data submission forms take minutes using services like FormSubmit.
- Add to calendar button web comoponent - The Next-level Add to Calendar Button. Make your events get saved!
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) vs. Mobile and Desktop Apps
In today’s digital ecosystem, users interact with various types of applications designed for different platforms and user experiences. Each format—Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), mobile apps, and desktop apps—has unique features and use cases, making it crucial to understand their differences. While mobile and desktop apps are typically native applications requiring dedicated development, PWAs offer a more versatile, cost-effective solution by combining the best of websites and apps.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs are web-based applications that leverage modern web technologies (like service workers, push notifications, and web app manifests) to deliver an app-like experience directly through the browser. PWAs can be installed on both mobile and desktop devices, offering offline functionality and access to hardware features such as geolocation, camera, and notifications.
Key Characteristics of PWAs:
- Responsiveness: PWAs automatically adjust to different screen sizes and resolutions, providing an optimized experience across mobile, tablet, and desktop devices.
- Offline Capability: Thanks to service workers, PWAs can cache assets and data, ensuring they function offline or in low-connectivity environments.
- No App Store Dependency: Users can install PWAs directly from a website by simply clicking an “Add to Home Screen” or “Install” prompt, bypassing the need for app store submission. This reduces distribution costs and complexities.
- Cost Efficiency: Rather than developing separate native apps for different platforms (iOS, Android, Windows), a single PWA works across all devices, saving development time and resources.
Installing PWAs on Mobile and Desktop Devices:
One of the standout features of PWAs is their ability to be installed directly from the web onto mobile and desktop devices, providing a seamless app-like experience without relying on app stores. Here’s how this works for both:
- On Mobile:
- Installation on Android: When a user visits a PWA-enabled website on an Android device, they may see a prompt offering the option to “Add to Home Screen.” After clicking this, the PWA is installed just like a native app, accessible directly from the home screen without the need for app store downloads.
- Installation on iOS: On iOS, the process is similar. Users can manually add a PWA to their home screen through Safari by selecting the “Add to Home Screen” option in the browser’s menu. While iOS doesn’t fully support all PWA features (e.g., background sync and push notifications), the installation still offers a native-like experience.
- On Desktop:
- Installation on Windows and macOS: PWAs can also be installed on desktop devices. On platforms like Windows and macOS, when a user visits a PWA-enabled site in a browser (such as Chrome or Edge), they may receive an option to “Install” the app. Once installed, the PWA operates as a standalone application, appearing in the system’s start menu (Windows) or applications folder (macOS), and can be launched without needing to open a browser. PWAs also support native desktop features, such as taskbar pins and notifications, depending on the browser.
- Mobile Apps
- Mobile apps are software applications designed specifically for smartphones and tablets. These apps are typically downloaded and installed from app stores such as Google Play or the Apple App Store. Mobile apps are optimized for performance and can access advanced hardware features, offering a tailored experience for users.
### Key Characteristics of Mobile Apps:
- Platform-Specific Development: Separate versions are generally required for iOS and Android, though frameworks like Flutter and React Native enable cross-platform development.
- Enhanced Performance: Native apps are optimized for specific devices and operating systems, providing high performance and responsiveness.
- Access to Advanced Features: Mobile apps can leverage device-specific hardware, like cameras, GPS, sensors, and biometric authentication.
- App Store Dependency: Distribution through app stores is required, and apps must adhere to store guidelines and pay associated fees.
Desktop Apps
Desktop apps are software programs designed to run on desktop or laptop computers. These apps are typically installed locally and often do not require an internet connection to function. Desktop apps are more feature-rich, making them ideal for complex tasks.
Key Characteristics of Desktop Apps:
- Platform-Specific Development: Similar to mobile apps, desktop apps are often tailored to specific operating systems like Windows, macOS, or Linux.
- High Performance: Desktop apps can handle resource-intensive tasks, such as video editing, 3D rendering, or large-scale data processing.
- Offline Usability: Desktop apps generally work offline, though some may require periodic syncing with a server.
- Distribution Flexibility: Some desktop apps are available through app stores, while others are distributed via direct downloads from the developer’s website.
### How PWAs Compare to Mobile and Desktop Apps
- PWAs vs. Mobile Apps: PWAs offer a more accessible alternative to mobile apps by allowing users to install the app directly from the website without going through app stores. They can work offline, access device features like push notifications, and provide a consistent experience across both mobile and desktop platforms. However, native mobile apps can deliver better performance, especially for resource-intensive applications like games or those requiring extensive use of hardware features (e.g., camera or GPS).
- PWAs vs. Desktop Apps: PWAs are increasingly capable of offering desktop-like experiences and can be installed directly on Windows and macOS systems. While desktop apps generally offer better performance and more advanced capabilities (especially for professional or creative tasks), PWAs can provide a sufficient, lower-cost alternative for many users. PWAs do not require regular updates or complex installation processes and are distributed entirely through the web.
Choosing the Right Format
The decision between a PWA, mobile app, or desktop app depends on factors such as target audience, functionality requirements, and budget:
- PWAs are ideal for businesses looking to reach a broad audience across platforms without the cost and complexity of developing separate mobile and desktop apps.
- Mobile apps are best for applications requiring high performance and advanced use of hardware features, such as games, camera-heavy apps, or apps with complex offline functionality.
- Desktop apps remain the best choice for power users who need robust, resource-intensive applications that require maximum performance and capabilities.
- By understanding the unique advantages and limitations of these different formats, businesses and developers can select the most effective way to deliver user experiences tailored to their goals and audience needs.
Using Tool for Rapid Product Development and Deployment
Modern tools like ShadUI and React Admin have transformed how developers and application designers create and deploy custom products. These tools streamline the process of building user interfaces, managing data, and scaling applications, enabling even complex projects to be completed with greater speed and efficiency.
Streamlined UI Development with ShadUI:
ShadUI offers a suite of ready-to-use, customizable components that help developers build visually appealing interfaces quickly. This reduces the time spent on designing and implementing UI elements from scratch, allowing teams to focus on delivering user-centric experiences. With its library of pre-built elements, ShadUI allows developers to adjust styles, themes, and components to fit the branding and design requirements of their products. This means that creating a custom-looking application becomes as easy as a few clicks, making the tool ideal for both prototyping and production-level design.
Efficient Data Management with React Admin
https://marmelab.com/react-admin/
React Admin is a powerful tool for building data-driven applications. It provides a framework for managing complex data structures, creating dashboards, and integrating APIs with ease. By leveraging React Admin, developers can quickly create admin panels, dashboards, and management systems that provide an intuitive backend for business operations. The tool’s flexibility in handling data sources and seamless integration with various RESTful APIs and GraphQL backends allows teams to manage large-scale applications with ease. This ability to handle data efficiently ensures that applications can scale as user demand grows, making it a great choice for products that need to reach a large audience.
Rapid Deployment and Scalability
Both ShadUI and React Admin are designed to work seamlessly with modern development workflows and cloud infrastructure, making it easier to deploy applications at scale. With cloud services like AWS, Google Cloud, and serverless platforms, developers can deploy their ShadUI and React Admin-based products in just a few steps. The ease of deploying custom-built applications means that businesses can quickly launch new features, updates, or entire applications, responding to user needs and market trends. This agility is crucial for businesses looking to maintain a competitive edge and ensure a smooth user experience as their customer base grows.
4 - Attribution: A Comprehensive Guide
When another website refers a customer to your business, it’s important to know which website it was and which marketing campaign or traffic source they used. By using custom applications and configuring the flow of the information you want, you can track it and give proper attribution to the referring property.
Platform click-throughs
While a click from a third-party platform may use a campaign to identify the traffic source, you can also use the platform that referred them to learn about the traffic.
For example, you can use Google Search Central to see your impressions and the queries they were for.
Marketing campaigns
This is especially useful for businesses that engage in affiliate marketing or partner with other websites to drive traffic and sales. By tracking the referrals and attributing them properly, you can ensure that your partners are receiving the credit they deserve for their efforts.
TLDR
In short, it answers: When a user is referred from another website, you get a referrer event in your analytics, but when that user makes a conversion elsewhere inside your website, how do you know which referrer to give credit to? The referring session might not be the one that ultimately makes a sale, since a user may leave your site and come back another time. To help capture the required data, you may employ methods to capture attribution data and then associate any user conversions within your website with a referer campaign. On the old internet, the ad tech could make a mark on a user session that the signal was from x about product y. Google, for example, is now proposing the following to aid with ad tech attribution without third-party cookies:
How does attribution allow measurement?
But attribution goes beyond just giving credit. It also provides valuable insights into which marketing campaigns and traffic sources are driving the most sales conversions. By analysing this data, you can optimise your marketing efforts and focus on the channels that are most effective.
Custom applications can help you track and analyse this data in real-time, giving you a clear picture of which referrals are converting into sales. This can help you make informed decisions about your marketing campaigns, adjust your strategies, and ultimately improve your overall performance.
So, if you’re looking for ways to improve your marketing campaigns and sales conversions, consider using custom applications to track and attribute referrals. By doing so, you can gain valuable insights and optimise your efforts for maximum impact.
Digital marketing attribution software
Attribution software is handled by ad tech platforms. You may find more information regarding this topic at our guide on analytics.
More information
5 - Contact page: Exploring the best contact methods
A contact page is a crucial element of a website that allows visitors to get in touch with you. It is an essential feature of any website, regardless of its purpose. A contact page provides a simple and efficient way for visitors to communicate with you, ask questions, provide feedback, and more. In this article, we will discuss the use cases for a contact page on a website.
Providing all accessibility formats
Providing information to all your potential customers requires using many formats. Including the web, phone, sign, email etc. Other decisions also play a role, are you happy to leave an email or phone number available to the public? Are there multiple contact points used by different people? Contact applications also work with other aspects of the web, to learn more about pass your details to search engines, you can view a guide on structured data.
To add a form to give users the ability to contact you instantly.
One of the main use cases for a contact page is to provide a form or method that visitors can fill out to contact you instantly. This form typically includes fields for name, email, subject, and message. The form can also include other fields depending on the purpose of your website. For instance, if you are running an e-commerce website, you can add a field for order number.
When adding functionality it is important to consider if what you are adding is imposing any conditions upon potential consumers. Having a form instead of an email may impose a restriction on senders to use other means to store a duplicate message or an indicator of the message. Taking into account that existing functionality already has better accessibility than your Implementation.
For some communication, like having a form which upon receiving a message, sends a receipt to an email including the contents, is not perfect accessibility to someone without an email or a postage stamp. Since the receipt was not generated from their side of the communication.
QR Codes and vCards
Another common format that users expect are vCards; vCards are the best digital business card format when transferring data from one medium to a user’s Contact application. Build a vCard here. QR codes can also be used with vCards for seamless sharing.
What should be on a contact page?
In a perfect world, making every method available would be preferred.Allowing users to quickly choose their preferred method. The contact page should be the definitive place users can refer to for any up-to-date details. Be sure to include links to all the methods you support. Humans aren’t the only thing that can use your contact page to receive information, search engines and other applications (see structured data) can access your information here.
Should social media links be included?
Another use case for a contact page is to provide a wide variety of details such as the phone number, physical address, and social media profiles. This information is essential for visitors who prefer to contact you using these methods. Providing multiple ways to contact you increases the chances of visitors getting in touch with you.
As more is better, consider methods to combine multiple profiles into one manageable one. However, it is advisable to be selective in your adoption of any platform.
Adding opening hours?
Your website should be the authoritative source of information on your business. Offering more info than other applications do and any further details. Other applications now offer information on your business but it’s effective for your website to be the source of any info. The aim of a good website is to create a rich authoritative document that utilizes exciting web features to provide functionality to customers. Providing enough utility to enable users to leverage value from web features is now more Important than ever.
Applications are getting smarter and more integrated every day. Still, no matter how smart AI applications and user feedback improvement become at determining and displaying information on your behalf, a source of truth must be called to provide the most up-to-date info. On the other hand, allowing customers to optimise functionality is imperative for competitiveness. Even those third party applications can’t work for the use cases where for example there’s been an unexpected closure. That is without making a call to a source of truth. Read more on structure.
The cost to make a network call is minuscule to the petrol cost of a wasted trip to the shopping mall.
A customer bookmarks your contact page, opening it to check if a shop is open just before having to enter the mall to get a coffee. If it’s closed, 5 mins could have been saved.
Take a customer traveling to a fast food restaurant, before engaging with any order there first needs to be a check on if its open. Else you risk frustrating a customer by wasting effort in creating a particular basket only to then force them to abandon it.
Or, to display a notice to potential visitors to redirect to an overflow car park.
Should A map be included on a website contact page?
If your business has a physical location, you can use your contact page to provide a map or directions to your location. This is particularly helpful for visitors who are not familiar with your area and need help finding your business.
To receive feedback from visitors.
Your contact page can also be used to receive feedback from visitors. This feedback can be about your products, services, website, or anything else related to your business. Feedback can be valuable in helping you improve your business and website.
To provide customer support.
If you offer customer support, your contact page can be used to provide this service. You can provide a phone number, email address, or live chat option for visitors to get in touch with your support team. This is particularly important for e-commerce websites, where visitors may have questions or issues with their orders.
In conclusion, a contact page is an essential component of any website. It provides a simple and efficient way for visitors to communicate with you, ask questions, provide feedback, and more. By including a contact page on your website, you can improve the user experience and increase the chances of visitors getting in touch with you.
6 - Messaging: Using Applications and Data Pipelines
In today’s complex business environment, gathering information and reports from multiple services can be challenging. While many services can generate information, the ability to receive timely notifications and collaborate effectively with teams is crucial. One emerging method to address this challenge is the use of messaging applications like Slack. These applications have evolved to be more than just simple messaging tools and now offer the capability to create rich data pipelines, enabling users to gain insights from various tools and services.
Benefits of Using Messaging Applications and Data Pipelines
Messaging applications such as Slack provide several benefits when integrated with data pipelines:
- Real-time Notifications: Users can receive immediate notifications when a service produces a report or when specific events occur, allowing for timely action and decision-making.
- Seamless Collaboration: With the ability to enrich messaging with plugins, users can configure rich data pipelines to facilitate seamless collaboration and information sharing within teams.
- Enhanced Insights: By integrating messaging applications with data pipelines, users can gain valuable insights from the generated reports and information, enabling informed decision-making.
Many services offer built-in notification systems that can be sufficient for tracking various metrics without the need for additional integrations. For instance, Google Analytics allows users to set up notifications that can be delivered through push messaging and email. This can be particularly useful for keeping track of website traffic changes, user behavior, or anomalies in data. By configuring alerts directly within Google Analytics, users can receive timely updates on key metrics without needing to rely on third-party messaging applications. Detailed instructions on how to set up these notifications can be found in the Analytics guide, making it easy for businesses to stay informed about their data.
The Forms of Messaging Applications
There are many types of messaging applications. The core technologies of the World Wide Web are messaging tech. As features are added to these core technologies, they become better suited to particular use cases. Some of the messaging forms that have remained in use are text messages, email, instant messaging, radio, morse code, etc, and web-based messengers.
Applications like Slack or Zoom represent the highest form of applications in terms of content possibilities. They include instant messaging capabilities and text message capabilities. Modern messaging applications include many more features and are more comparable to web browsers. While this type of messenger sounds great, the complexity comes at a cost. Each messenger limits your freedom to the features of that particular service. Standardization attempts are occurring but have been very slow. This makes any migration to other services a costly endeavour that often results in losing a considerable amount of information.
Key Considerations for Using Messaging Applications and Data Pipelines
When utilizing messaging applications and data pipelines, there are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the messaging application is capable of integrating with a wide range of tools and services to create comprehensive data pipelines. Modern applications like Slack provide built-in plugins that are supported by many leading services. These plugins allow the user to enable the services without any custom development. The user interface allows permission to be granted, which can then access the service APIs (usually via the OAuth2 protocol). Once an application has permissions it can start receiving messages.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information from being shared and accessed through messaging applications and data pipelines. When allowing access from one service to another, make sure the permissions are as restrictive as possible. Also, consider implementing multi-factor authentication and encryption to ensure comprehensive security for the shared and accessed information.
- Scalability: Evaluate the scalability of the chosen messaging application and data pipeline infrastructure to accommodate the growing needs of the organization.
Best Practices for Implementing Messaging Applications and Data Pipelines
To maximize the effectiveness of messaging applications and data pipelines, consider the following best practices:
- Customized Notifications: Tailored notifications can be configured to deliver specific and relevant information to the appropriate individuals or teams, ensuring that they receive the updates they need to stay informed and take necessary actions. Additionally, custom plugins can be written to work with custom services that provide anything that the messaging app supports. Messaging applications themselves support rich application widgets, further enhancing the user experience.
- Automation: Utilize automation capabilities within the data pipelines to streamline the process of gathering and disseminating reports and information. For example, using Google Analytics to send insight reports while also utilising Google Cloud Platform Alerting. This ensures that you are in the loop and that if the notifications from one service have failed to reach you, another service may succeed.
- Inclusivity: Enable diverse discourse around critical factors by allowing access to insights and conversations for everyone involved. This can foster a collaborative environment and ensure that various perspectives are considered.
- Leveraging Service Capabilities: By understanding the capabilities of your services, you can create rich metrics that provide a stream of automated actionable intelligence. Each business can develop unique streams of information that leverage their key focus. For instance, you can connect an RSS feed of industry news to the “news” channel, while custom curated report summaries are sent in real time to the “sentiment” channel. Combining this with AI sentiment analysis and traditional data science services, often administered by business staff and applied to web page design, can result in a compelling and efficient system.
Connect Your Team With Messaging Applications
- Using Slack.com
- Connect application using built in Slack plugins
- Connect other Services Like Google Analytics
Conclusion
Messaging applications, when integrated with robust data pipelines, offer a powerful solution for gathering information and reports, as well as facilitating effective collaboration and insights within teams. By leveraging the capabilities of messaging applications like Slack and enriching them with data pipelines, organizations can optimize their operational efficiency and decision-making processes.
7 - Tools: A guide on handy website features
In today’s world, businesses are constantly looking for ways to add value to their customers. One way to do this is by creating tools or computations that can provide value to customers. These tools can help customers navigate complex situations and make better decisions. They can also improve trust between businesses and their customers.
Tools and computations can take many forms. They can be spreadsheets, calculators, data visualizations, or even simple web applications. Whatever form they take, the goal is always the same: to provide value to customers.
One advantage of these tools is that they can be created relatively easily. Many businesses already have spreadsheets or other computations that they use internally. These can often be repurposed and turned into more user-friendly applications for customers.
For example, a financial advisor might have a complex spreadsheet that they use to calculate retirement savings. This spreadsheet could be turned into a web application that allows customers to input their own data and get personalized retirement savings projections. This tool would provide value to customers by helping them make better retirement planning decisions.
Another advantage of these tools is that they can help build trust between businesses and their customers. When customers see that a business has created a tool that is designed to help them, they are more likely to trust that business. This can lead to increased loyalty and repeat business.
For example, a real estate agent might create a tool that allows customers to see historical property values in a particular area. This tool would provide value to customers by helping them make more informed decisions about property purchases. It would also help build trust between the agent and the customer by demonstrating the agent’s expertise and commitment to helping the customer.
In conclusion, any tool or computation that a business creates can provide value to customers. These tools can take many forms and can be repurposed from existing internal computations. They help customers navigate complex situations and make better decisions, while also building trust between businesses and their customers. By creating these tools, businesses can improve the customer experience and increase loyalty and repeat business.
8 - Calendar: How to Use a Calendar with Your Website
Why Add a Calendar to Your Website?
Adding a calendar to your website provides numerous benefits:
- Convenience: Visitors can quickly view events or schedule appointments.
- Automation: Sync schedules and reduce manual updates.
- Professionalism: Build credibility by showcasing a well-organized interface.
- Engagement: Encourage users to interact with your website.
Steps to Add a Calendar to Your Website
1. Choose the Right Calendar Tool
Decide on the type of calendar that best suits your needs:
- Static Calendars: Great for displaying fixed events.
- Interactive Calendars: Ideal for dynamic schedules, allowing users to interact (e.g., book appointments).
2. Embed a Calendar
Most calendar services offer an embed option, letting you add their calendar widget to your site or will provide the calendar on a website they provide which can be linked to. For example, Google Calendar provides HTML code that can be copied and pasted into your website:
- Go to Google Calendar.
- Click on the settings for the calendar you want to embed.
- Find the “Integrate calendar” section. See Integrating with a Service Provider section below
- Copy the embed code.
- Paste the code into your website’s HTML at the desired location.
If you don’t have access to your website’s HTML or prefer to consult an expert, consider reaching out to a developer.
Below, you can book an appointment with me through the integrated calendar or reach out via my contact page.
3. Customize the Design
Ensure the calendar matches your website’s design by customizing colors, fonts, and layout. Many calendar tools offer configuration options directly in their settings, or you can use CSS to modify the embedded calendar.
4. Make It Responsive
Optimize the calendar for all devices by using responsive design principles. Add CSS rules to ensure the calendar adjusts well to various screen sizes.
Integrating with a Service Provider
Why Use a Service Provider?
Services like Google Calendar or Google Appointments provide robust APIs, automatic syncing, and cross-platform accessibility. These integrations allow you to:
- Automatically update events on your website.
- Allow users to book appointments seamlessly.
- Sync events with other tools or devices.
Adding Google Appointments
Google Appointments streamlines booking by letting users select time slots directly from your website. Follow these steps:
- Set Up Appointment Schedules
- Log in to Google Calendar.
- Click on a date and select “Appointment Schedule.”
- Customize the available time slots and add details.
- Share Appointment Links
- Obtain a link to your appointment schedule.
- Embed the link or button on your website for easy access.
- Automate Confirmation Emails: Google automatically sends booking confirmations and reminders, saving you time.
See help guide.
Once you’ve followed the guide, you can share the link via email, text, or any preferred method. Use DNS forwarding to create short, user-friendly URLs—for example, appointment.mywebsite.com forwarding to your long Google Calendar link (your-super-long.google.com/calendarlink?aisfbalsibn23ihur23irbasfd).
For example, sending the URL book.snowdon.dev to https://calendar.app.google/ECgv242NeFTyfNYF7, much easier to remeber. Learn more about hyperlinks here.
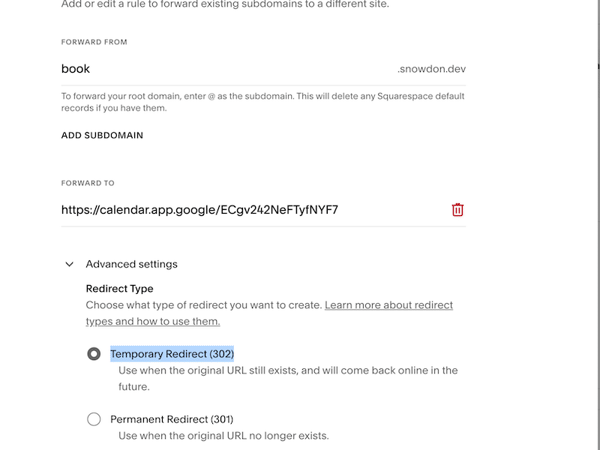
Using Squarespace to set up a DNS redirect that forwards your custom domain to a Google Appointment Booking screen.
The Google Appointment setup includes snippets of code that can be easily embedded into your website, like this:
<!-- Google Calendar Appointment Scheduling begin -->
<link href="https://calendar.google.com/calendar/scheduling-button-script.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://calendar.google.com/calendar/scheduling-button-script.js" async></script>
<script>
(function() {
var target = document.currentScript;
window.addEventListener('load', function() {
calendar.schedulingButton.load({
url: 'https://calendar.google.com/calendar/appointments/schedules/AcZssZ3CnePJHrc5V3FAUsRtwhf1VEmyHpA5LftczZeDidG8_3gQ_ZCVT_mpr7sCkvn--myoF6ih7P4T?gv=true',
color: '#039BE5',
label: 'Book an appointment',
target,
});
});
})();
</script>
<!-- end Google Calendar Appointment Scheduling -->
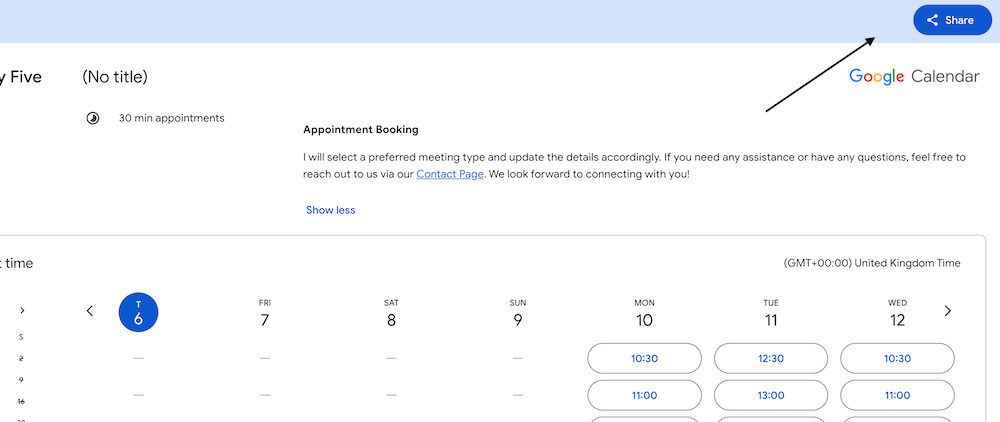
Once you’ve created your appointment schedule in Google Calendar or Google Appointment Scheduler, find the share link:
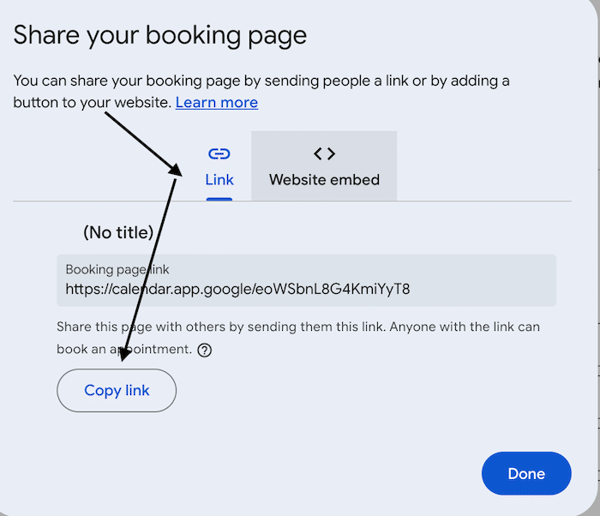
Then grab either the code snippet for adding to your website, or the URL for adding to the DNS forwarding.
Steps to Integrate with Google Calendar
This section details how to programmatically edit the calendar. This is necessary for creating automation changes that align with your business processes. For example, you can create a calendar for specific users when they sign up to your website (or pay a price) and populate it with events that handle business transactions, such as due dates or delivery times.
1. Obtain API Access
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Create a new project and enable the Google Calendar API.
- Generate API credentials (OAuth 2.0 client ID or API key).
2. Install a Client Library: For websites using JavaScript
<script src="https://apis.google.com/js/api.js"></script>
3. Authenticate Users
Allow users to log in and connect their Google account to your website. Use Google’s OAuth flow for secure authentication.
4. Display Events on Your Website
Use the Google Calendar API to fetch and display events dynamically - for example on a admin page to create new events, the code may look like:
gapi.load('client', () => {
gapi.client.init({
apiKey: 'YOUR_API_KEY',
discoveryDocs: ["https://www.googleapis.com/discovery/v1/apis/calendar/v3/rest"]
}).then(() => {
return gapi.client.calendar.events.list({
calendarId: 'primary',
timeMin: (new Date()).toISOString(),
showDeleted: false,
singleEvents: true,
maxResults: 10,
orderBy: 'startTime',
});
}).then(response => {
const events = response.result.items;
console.log(events);
// Display events on the page
});
});
5. Sync User Bookings
Allow users to create or edit events directly from your website:
gapi.client.calendar.events.insert({
calendarId: 'primary',
resource: {
summary: 'New Appointment',
start: { dateTime: '2024-12-31T10:00:00-07:00' },
end: { dateTime: '2024-12-31T11:00:00-07:00' }
}
}).then(response => {
console.log('Event created:', response);
});
This approach can be extended to automate workflows such as creating personalized calendars for new users or setting up default events based on your business logic (for example when a user signs up they get their own calendar and events for deliveries or due dates).
How the browser handles creating events
Desktop versions of Chrome and Safari don’t have native functionality to directly create calendar events from a plain string of text. However, you can achieve this functionality through various approaches, depending on your needs.
1. Add an “Add to Calendar” Link
You can provide a link or button that uses calendar service APIs (e.g., Google Calendar, Outlook) to create an event from a string of text. This is straightforward and works in all modern browsers.
Example: Google Calendar
<a href="https://calendar.google.com/calendar/render?action=TEMPLATE&text=Event+Title&details=Description&location=Location&dates=20241231T235900Z/20250101T005900Z" target="_blank">
Add to Google Calendar
</a>
- text: Event title.
- details: Event description.
- location: Event location.
- dates: Start and end time in ISO 8601 format (YYYYMMDDTHHmmssZ).
Example: iCal File Download (Works with Calendar Apps)
Create and link to an .ics file, which users can download and open in their default calendar app.
<a href="event.ics" download="event.ics">Add to Calendar</a>
Example .ics file content:
BEGIN:VCALENDAR
VERSION:2.0
PRODID:-//YourOrganization//NONSGML v1.0//EN
BEGIN:VEVENT
UID:12345@example.com
DTSTAMP:20241231T000000Z
DTSTART:20241231T235900Z
DTEND:20250101T005900Z
SUMMARY:Event Title
DESCRIPTION:Event Description
LOCATION:Event Location
END:VEVENT
END:VCALENDAR
2. Enable Interaction via JavaScript
If you want to allow users to select text and create an event programmatically, you can use JavaScript to parse the text and construct a calendar event.
Example: Google Calendar Integration
document.querySelector('#createEventButton').addEventListener('click', () => {
const eventTitle = "Sample Event";
const eventDetails = "This is an example event created from text.";
const eventLocation = "New York, NY";
const startDate = "20241231T235900Z"; // UTC format
const endDate = "20250101T005900Z"; // UTC format
const googleCalendarUrl = `https://calendar.google.com/calendar/render?action=TEMPLATE&text=${encodeURIComponent(eventTitle)}&dates=${startDate}/${endDate}&details=${encodeURIComponent(eventDetails)}&location=${encodeURIComponent(eventLocation)}`;
window.open(googleCalendarUrl, '_blank');
});
Example: Dynamic Event Creation from Text Input
<input type="text" id="eventInput" placeholder="Enter event title">
<button id="createEvent">Create Event</button>
<script>
document.querySelector('#createEvent').addEventListener('click', () => {
const input = document.querySelector('#eventInput').value;
const eventTitle = encodeURIComponent(input || 'New Event');
const startDate = "20241231T235900Z"; // Default UTC start time
const endDate = "20250101T005900Z"; // Default UTC end time
const url = `https://calendar.google.com/calendar/render?action=TEMPLATE&text=${eventTitle}&dates=${startDate}/${endDate}`;
window.open(url, '_blank');
});
</script>
3. Leverage Browser Extensions
For users to create events from selected text, recommend using a browser extension or bookmarklet. Some popular options:
- Google Calendar Extension: Allows event creation from selected text directly in Chrome.
- Shortcut Bookmarklet: Write a JavaScript bookmarklet that parses the selected text and redirects to a calendar service.
Example Bookmarklet Code:
javascript: (function () {
const text = window.getSelection().toString();
const url = `https://calendar.google.com/calendar/render?action=TEMPLATE&text=${encodeURIComponent(text)}`;
window.open(url, '_blank');
})();
4. Use Natural Language Parsing (Advanced)
Services like OpenAI API or Chrono.js can parse free-form text into structured data for event creation.
Example with Chrono.js
const text = "Meeting at 3 PM on December 31 in New York";
const parsed = chrono.parseDate(text);
if (parsed) {
const startDate = new Date(parsed).toISOString().replace(/[-:]/g, '').split('.')[0] + 'Z';
const googleCalendarUrl = `https://calendar.google.com/calendar/render?action=TEMPLATE&text=Parsed+Event&dates=${startDate}/${startDate}`;
window.open(googleCalendarUrl, '_blank');
} else {
alert("Could not parse date/time.");
}
5. Override the selection to provide menu option
document.addEventListener('selectionchange', function() {
const selc = document.getSelection();
const range = selc.getRangeAt(0)
const container = range.startContainer;
if (isNotSelectable(container)) {
return
}
const text = window.getSelection().toString();
const url = `https://calendar.google.com/calendar/render?action=TEMPLATE&text=${encodeURIComponent(text)}`;
openMenu(url, "Google Calendar Event")
});
Summary
To enable event creation in Chrome or Safari:
- Add a link or button to services like Google Calendar or download an .ics file.
- Use JavaScript to dynamically construct URLs or handle user input.
- For advanced needs, parse natural language with libraries like Chrono.js.
Creating event on iPhone
To create text that an iPhone can recognize and use to create an event, you need to format the information in a way that iOS can detect as event data. This typically involves leveraging Data Detectors in iOS. These detectors recognize certain patterns, like dates, times, and event-related phrases, and provide users with options to interact with the content (e.g., creating calendar events).
Strategies for Event Creation on iPhone
1. Plain Text with Date and Time
iPhones can detect simple date and time mentions in plain text. When a user taps on such text, iOS prompts them to add the event to their calendar. Example:
Meeting with Sarah on December 31, 2024, at 2:00 PM.
To maximize detection:
- Use standard date and time formats (December 31, 2024, at 2:00 PM).
- Include specific event-related words like “meeting,” “appointment,” or “event.”
2. HTML
The
Example:
<p>Meeting with Sarah at <time datetime="2024-12-31T14:00:00+00:00">2:00 PM UTC</time>.</p>
When viewed on an iPhone, this can provide additional interactivity for calendar integration.
3. Calendar File (.ics)
You can provide a downloadable .ics file, which is the universal standard for calendar events. iPhones automatically open .ics files in the Calendar app, making it easy for users to add events.
Example .ics File:
BEGIN:VCALENDAR
VERSION:2.0
PRODID:-//YourOrganization//NONSGML v1.0//EN
BEGIN:VEVENT
UID:12345@example.com
DTSTAMP:20241231T000000Z
DTSTART:20241231T140000Z
DTEND:20241231T150000Z
SUMMARY:Meeting with Sarah
DESCRIPTION:Discuss the project details.
LOCATION:Office
END:VEVENT
END:VCALENDAR
Steps to Use:
- Save the content above to a file named event.ics.
- Provide a download link on your website or email:
<a href="event.ics" download="Meeting with Sarah.ics">Add to Calendar</a>
4. Event Link for Calendar Services
Direct links to calendar services like Google Calendar or Microsoft Outlook also work on iPhones and prompt users to add the event.
Example Google Calendar Link:
<a href="https://calendar.google.com/calendar/render?action=TEMPLATE&text=Meeting+with+Sarah&details=Discuss+the+project+details.&location=Office&dates=20241231T140000Z/20241231T150000Z">
Add to Google Calendar
</a>
5. Siri and Shortcuts Integration
If you control the device or app, you can create integrations using Siri or the Shortcuts app:
- Provide a shortcut that parses natural language or .ics data and adds it directly to the Calendar app.
Tips for Compatibility
- Use Natural Language: Write dates and times explicitly in a natural, unambiguous way. Good: “Meeting on December 31, 2024, at 2:00 PM.” Avoid: “Meeting next Tuesday at 14:00.”
- Include Time Zones: Always specify the time zone if the event involves users in multiple regions.
- Test on Devices: Ensure the text or file is properly recognized by trying it on an actual iPhone.
Conclusion
Integrating a calendar with your website enhances usability, simplifies scheduling, and keeps users engaged. By embedding a calendar or leveraging services like Google Calendar and Google Appointments, you can create a seamless experience for your visitors. Take the time to customize and optimize your calendar for maximum impact!
9 - Structure: Methods of custom analysis
The internet has become an integral part of our daily lives and the amount of information available online is increasing at an unprecedented rate. Websites are the primary medium for disseminating information online, and they must adhere to certain standards to ensure their content is accessible and valuable to all users. To achieve this, analysis of structured website documents is necessary to test against many different standards.
Structured website documents are created using specific markup languages like HTML, XML, and XHTML. These languages define how the content is presented on the web page. For instance, HTML tags are used to define the structure and layout of the web page, while XML tags define the data structure of the web page. XHTML is a combination of HTML and XML. By analyzing the structured website document, we can ensure that the content is structured correctly, and it adheres to the required standards.
Creating unique and custom analysis has great benefits on the standards of the content produced and the value it gives. Custom analysis allows developers to check the website against specific standards that are relevant to their project. For example, accessibility standards ensure that the website is accessible to users with disabilities. This is particularly important for websites that provide critical services, like government websites, news websites, and medical websites.
Custom analysis also allows developers to test against different versions of the same standard. For example, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) have different versions, and each version has different requirements. By testing against different versions of the same standard, developers can ensure that their website is accessible to as many users as possible.
Moreover, custom analysis allows developers to test against multiple standards simultaneously. For example, accessibility standards and search engine optimization (SEO) standards can be tested simultaneously. This ensures that the website is not only accessible to users but also visible to search engines. This increases the website’s visibility and improves its ranking on search engines.
In conclusion, analysis of structured website documents is essential to ensure that the content is accessible and valuable to all users. Creating unique and custom analysis has great benefits on the standards of the content produced and the value it gives. It allows developers to test against specific standards, different versions of the same standard, and multiple standards simultaneously. This ensures that the website is accessible to as many users as possible and visible to search engines, thereby increasing its value.
10 - QR Codes: Enhancing User Experience and Accessibility
In today’s digital world, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are constantly seeking innovative ways to engage their customers and streamline their operations. One such tool that has gained popularity in recent years is the QR (Quick Response) code. These pixelated, square-shaped symbols have become a ubiquitous part of modern marketing strategies and have proven to be an effective and versatile tool for businesses of all sizes, including SMEs.
QR codes are perfect for facilitating contactless actions without requiring extensive user input. By simply pointing a camera at the QR code and clicking, users can access information, make payments, or perform various other actions with ease. This contactless nature makes QR codes convenient for users and can enhance the overall customer experience.
Furthermore, QR codes offer a multitude of functions, such as providing access to websites, downloading apps, sharing Wi-Fi network details, making payments, adding calendar events, and much more. Their versatility makes them an ideal tool for businesses looking to provide quick and efficient ways for customers to interact with their products and services.
What are QR codes?
QR codes are two-dimensional barcodes that can store a variety of information, such as website URLs, contact information, or product details. QR codes are designed to be scanned using a smartphone or a dedicated QR code scanner. Once scanned, the QR code can direct users to a website, display text, or trigger a specific action, making it a powerful and versatile tool for businesses.
Open the snowdon.dev vCard
Using your Camera
1. Click the link that appears around the QRCode. 2. Point your camera at the QR code
Using QR codes.
QR codes can be used in many formats and can invoke multiple application on many modern devices. On the go like devices (phones, tablets) and even VR (virtual reality) have the best support for QR codes. Many of the dollars of investment spent by the major players have went into VR technology, making the support QR codes almost ubiquitous.
There are many ways you can utilise this technology, and the best way will always be dependant on your business or your customers. From printing them out and displaying them in appropriate places. To using them within adverts and digital displays.
Warning: trust & security
When printing a QR code and displaying it on a medium (like a printout or sign), there is no mechanism to validate the origin of the QR code. Unlike when using web browsers, when using a printout, there is no asymmetric encryption to validate that a domain is owned by the current domain owner. Websites validate using certificates when making each request (during SSL secure socket layer) when the medium is viewed. If you want the viewer to trust what’s on the QR code, they need to trust what they scan the code from. Like an enclosed tablet or monitor display. Or from an email from a domain they trust. View our guide on hyperlink security to learn more about website security.QR codes, when scanned, can be acted upon based on its encoded data. Some of the many ways are as follows:
- Opening Apps
- Opening files
- Opening websites pages
- Opening any URL
- Opening raw text.
- Opening SMS client with a pre-generated message
- Opening a mail client with a pre-generated contents
- Opening a telephone number
- Opening an application
- Make payments with providers like PayPal.
- Inviting people to an event
- Connect to WiFi network
- Opening a vCard contact file in the default contacts app
QR codes have become an increasingly popular tool for bridging the physical and digital worlds. In many ways, QR codes serve as a practical bridge from physical images to digital content, similar to how hyperlinks function on the web. Just as hyperlinks can perform various functions, QR codes offer a range of capabilities. In fact, the range of functions they offer is almost identical. For instance, integrating QR codes and hyperlinks into emails or letters can save recipients time and effort by allowing them to quickly access links on their smartphones without the need for manual entry. This added convenience can greatly improve the overall user experience. It’s the difference between finding your glasses, typing out a large URL, correcting any mistakes, and doing so perhaps multiple times, versus simply looking in the direction and invoking an action. Including the ability to use multiple touchpoints provides added accessibility, which allows more users to engage with your product, and improves the options for people with disabilities.
Generate your own QR-Codes
Using our vCard and QR code generator application. Check here to start now. Completely free online tools.You may also quickly create QRCodes using applications you already have. For example, using Google Chrome you may right click on a page to create a QRCode that links to that page URL.
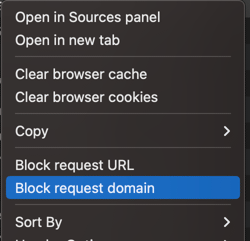
Right click on a web page. Using Google Chrome.
In Google Chrome - Menu -> Cast, save and share -> Create qrcode -> Downlaod
Using QR codes on their websites?
QR codes can be displayed on a web page for consumption by a user. This gives the admin of the website the ability to easily change the QR code and the page it is placed on. This means that there is no need to reprint the pages or distribute the email marketing campaign again. This technique is sometimes called dynamic QR codes, because the QR code is generated by a server, it can change the qr code and its parameters to whatever is desired at the time. It can also use other server features to customise the particular qr code based on information that is available (time, demographics). Users in the UK get one coupon, other users can a difference coupon. This coupon is only displayed and valid until 10am.
Another way a QR code can be used is by providing a URL that, when the QR code is scanned, takes them to a page. This is done by providing a valid URL encoded within the QR code. When this is scanned by a compatible device, it can open the URL. This is a great way to enable users to open your website without having to type in a URL or to share your page with another user. Because any URL can be added to QR codes, they can link to any page on your website, depending on the QR code that is scanned.
Integrating QR codes into a website can offer SMEs several benefits, including:
- Enhanced customer engagement: SMEs can use QR codes to provide additional information about their products or services. For example, a QR code on a product’s webpage can lead customers to a demonstration video, customer reviews, or related products, enhancing their overall experience.
- Contactless transactions: With the ongoing emphasis on contactless interactions, SMEs can use QR codes to facilitate transactions. By embedding QR codes that link to payment portals or order forms on their website, SMEs can provide customers with a convenient and safe way to make purchases.
- Promotional campaigns: QR codes can be integrated into promotional materials, such as flyers, posters, or social media posts, to drive traffic to a company’s website. SMEs can create QR codes that offer exclusive discounts, access to downloadable content, or entry into contests to incentivize customer engagement.
- Gathering customer data: SMEs can use QR codes to collect valuable customer data. By linking QR codes to surveys or feedback forms on their website, SMEs can gain insights into customer preferences, satisfaction levels, and areas for improvement.
- Word of mouth: By giving users and existing customers access to certain coupons, they are incentivized to share them with their friends. It serves as a great reason to share a link with someone. “Here, you can get 20 pounds off with this.”
Best practices for implementing QR codes on SME websites:
When incorporating QR codes into their websites, SMEs should consider the following best practices:
- Ensure mobile optimisation: Since QR codes are primarily scanned using smartphones, it is crucial to optimise the linked website for mobile devices. The landing page should be responsive, user-friendly, and designed to provide a seamless experience for mobile users.
- Provide valuable content: The content or action triggered by the QR code should add value to the user’s experience. Whether it’s exclusive discounts, additional product information, or engaging multimedia content, SMEs should ensure that the linked content is relevant and compelling.
- Track and analyse performance: Using analytics tools, SMEs should track the performance of their QR code campaigns. By monitoring metrics such as scan rates, conversion rates, and user engagement, SMEs can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their QR code strategies and make data-driven decisions for future initiatives.
- There are multiple types of coupons: those designed to be shared and those that are tailored and restricted (for example, a coupon only valid for enterprise customers doing over $1 million in business). Ensure your coupons and backend systems are designed to handle the coupons finding their way into the hands of someone they aren’t intended for.
In conclusion, QR codes offer SMEs a simple yet powerful tool to enhance customer engagement, streamline transactions, and gather valuable insights. By strategically incorporating QR codes into their websites and marketing efforts, SMEs can harness the potential of this technology to drive growth and create meaningful interactions with their target audience.
11 - Leveraging Digital Business Cards (vCards) for Success
In the digital age, the way businesses and professionals exchange contact information has evolved significantly. Virtual business cards, or vCards, have emerged as a sophisticated and efficient alternative to traditional paper cards. This article explores the benefits and practical applications of vCards in the modern business landscape. Additionally, it’s worth noting that the vCards format is constantly evolving, with current draft proposals to standardize newer features that contact applications have adopted.
What is a digital business card (vCard)?
A vCard is a simple format for exchanging information about contact details from one application to another. This means it’s represented as a data blob similar in format to .txt files. The standards have been developed independently by many different vendors, the lack of compatible feature support across devices has made it hard to create files on one device and expect that they will work everywhere they’re downloaded. However, this doesn’t mean the vCard isn’t relevant. They still have relevance when exchanging contact data between agents (devices), even if the agent only supports the old version 3 standard. vCards can even be used with Quick Response codes.
Working with vCards
Virtual business cards can contain metadata that enables them to be effectively used by machine agents. To fully leverage this, it’s essential to be aware of these properties. Each card is assigned a unique identifier (UID) and revision property (REV) to associate it with a specific identity and update sequence. When an application encounters a card with the same identifier, it can be assumed to relate to the same identity. This feature allows the application to support multiple functions, such as updating the information of a vCard when a new version becomes available or relating a vCard to another vCard. However, this also means that when changing any vCards, you must retain the UID. It’s necessary to load your existing vCard to avoid creating a separate vCard whenever someone imports your card.
Convenience and Accessibility
vCards offer great convenience for sharing contact information. They can be easily sent via email, SMS, websites, messenger, or social media, allowing recipients to save your contact details directly to their devices without having to type them in manually. This makes sure that your information is always easily accessible to your clients and colleagues, reducing the risk of losing or entering incorrect data. It’s more than just transferring data - with a contact application built into devices, this information can be used to enhance other experiences. For example, Maps can recognize that an address is linked to a specific person.
The possibilities are endless. You can add links to all your services and actions. Using templates, you can quickly create vCards that contain a similar set of links to your primary services and actions. This enables your customers to access everything they need at the touch of a button.
The interface to download a vCard differs between devices; it’s currently best supported on the iPhone. On desktops and other devices, it will fallback to downloading a file, which must be opened as usual to import the contact into a contact application.
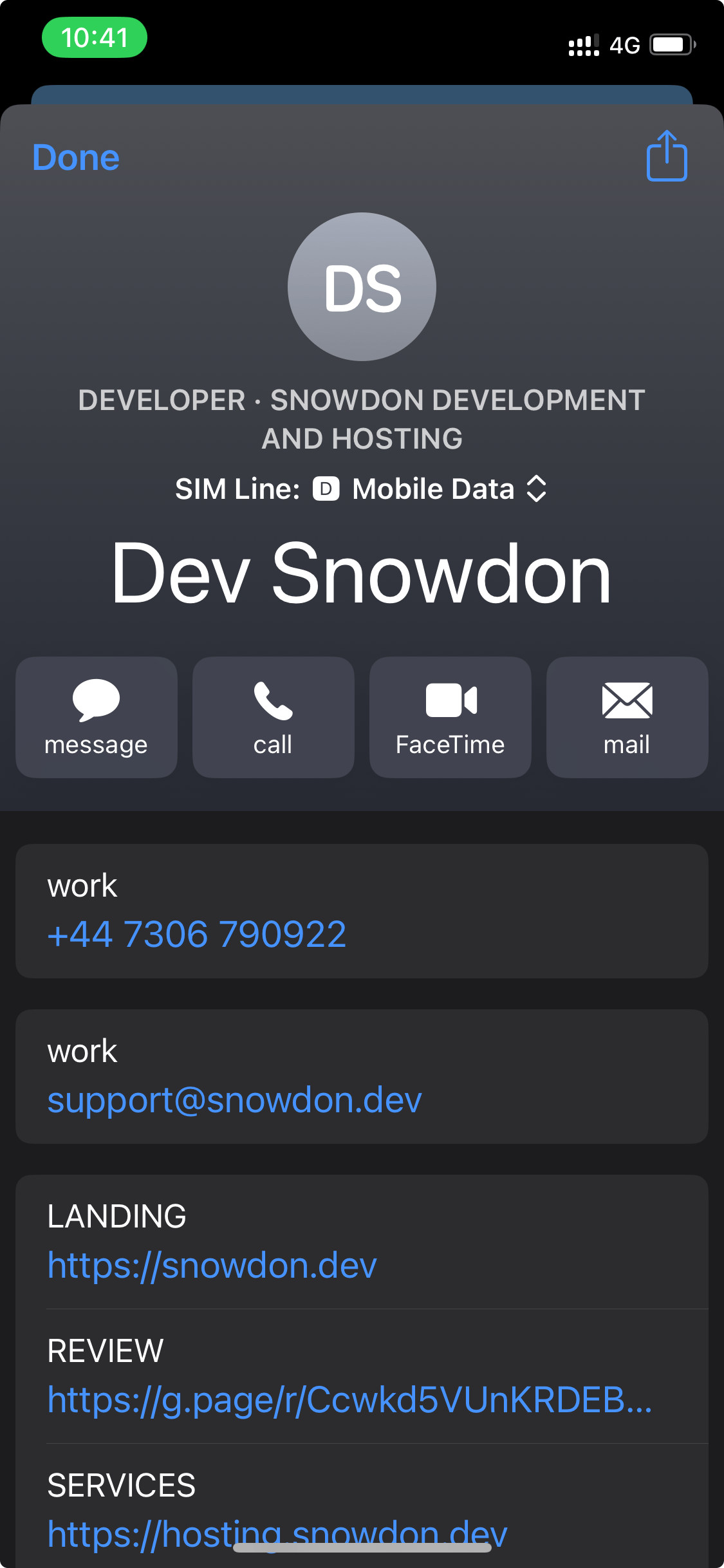
The view of a iPhone after pressing download.
Enhanced Professionalism
Using vCards demonstrates that your business is tech-savvy and environmentally conscious. It signals to clients and partners that you embrace modern tools and are committed to sustainability by reducing paper waste. This can enhance your brand’s image and appeal, especially to eco-conscious customers.
vCards are compatible with various digital platforms and devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers. They can be integrated into email signatures, websites, applications, and social media profiles, providing multiple touchpoints for potential clients to access your information. This seamless integration ensures that your contact details are readily available across all digital channels. Additionally, vCards can be version managed and include links back to the virtual address of the contact, enhancing the accessibility and functionality of the contact information.
Customizable and Updateable
Unlike traditional business cards, vCards can be easily updated with new information. Whether you change your phone number, email address, or job title, a simple update ensures that all your contacts have the latest information. Customization options also allow you to include logos, images, URLs, and additional details such as social media links, enhancing the card’s utility and branding.
Efficient Networking
Networking becomes more efficient with vCards as they facilitate quick and easy exchange of information during events, conferences, or casual meetings. Scanning a QR code or tapping a NFC-enabled device can instantly share your vCard, making the process swift and contactless—a significant advantage in today’s health-conscious environment.
Cost-Effective
While there is an initial cost associated with creating a vCard, the long-term savings are significant. There is no need for continuous printing and reprinting of paper cards, which can be costly and environmentally taxing. The digital nature of vCards ensures that you can distribute an unlimited number of cards without additional costs.
Practical Applications of vCards
Sales and Marketing
Sales professionals can use vCards to ensure that potential clients have instant access to their contact information, portfolio, and social media profiles. This immediate access can enhance follow-up rates and facilitate smoother communication.
Human Resources and Recruitment
HR departments can use vCards to streamline the recruitment process. Including vCards in job postings or emails ensures that candidates have easy access to recruiter information, making the process more professional and efficient.
Event Management
For event organizers, vCards can be included in event apps or QR codes on badges, allowing attendees to quickly exchange information and network more effectively.
Customer Service
Customer service teams can use vCards to provide clients with direct contact information, ensuring swift and personal customer support.
Job Site Storage
Adding your timesheet links and support documents offers a modern way to store and send all the information relating to a job or event. Mixing with the traditional features allows you to transfer all the details of an event, like a job address or the contact details. All in one handy place.
Newsletter and quick links
When sharing information with your clients, provide them not only with a link to your website homepage, but also include links to customer satisfaction surveys where they can provide feedback, and mailing list subscriptions so they can stay updated on the latest news and offers from your business. By including these additional links, you give your clients multiple avenues to engage with your business and provide valuable input while staying connected.
How to use vCard properties
The vCard format is widely used for sharing contact information electronically. While many of its properties are straightforward, some involve complex structures that can be challenging to implement and understand. Properties like FN (full name) or TEL (telephone) are easy to use because they follow simple formats. However, other properties, especially those that integrate with domain names, are much more intricate.
Simple vCard Properties
For basic contact information, the vCard format is user-friendly. Properties such as:
- FN: The full name of the individual.
- TEL: The phone number.
- EMAIL: The email address.
- ADR: The physical address.
These fields are widely understood and easy to populate. They follow predictable and straightforward patterns.
Complex vCard Properties: Domain Names and Protocols
However, the complexities begin when dealing with fields like EMAIL and URL that integrate with domain name systems (DNS). Domain names allow vCard fields to support multiple standards, providing advanced functionalities.
For instance:
- EMAIL: Can use various email formats based on domain configurations.
- URL: Can support multiple protocols and services depending on the domain.
Role of Domain Names in vCard
While it’s possible that any application or service can offer the interface that domain names provide, for example a proxy, it’s widely understood as the standard to use the domain name system. It’s built into the internet protocols and provides the greatest redundancies. The domain name system (DNS) plays a central role in managing and routing information in a vCard. DNS operates using records stored in a centralized registry, which are used to resolve the addresses of systems sending messages to the endpoints defined within that registry. When an entity creates a vCard with a domain name in the EMAIL or URL fields, it is essentially pointing to an interface controlled by the domain owner.
Example of Domain Control
Let’s consider an organization with several departments. When the entity behind an email address changes, such as during an organizational restructuring, the control of the domain allows for flexible redirection. Each department can set up forwarding rules so that their emails are directed to separate inboxes. The centralization of domain control ensures that these transitions happen seamlessly without requiring individual users to update their vCards. For example, if an organization takes over a subsidiary, it can forward emails from multiple departments to appropriate new addresses, all while maintaining a unified domain. This becomes critical when dealing with different inboxes for various departments, ensuring smooth communication during transitions.
An example of how the domain system can facilitate an interface between an address and the endpoint:
flowchart TD
A[vCard] -->|contacts| B["endpoint#64;domainname.com"]
B --> C{Requests address registered in the central registry}
C -->|forwards to the endpoint| D[test#64;gmail.com]
The Challenge of Complex Formats
The complexity arises when one considers the range of records and standards that can be used within a domain. DNS supports a variety of record types (e.g., MX records for email) that dictate how systems interact with the domain. For someone unfamiliar with these underlying protocols, configuring a vCard to take full advantage of these features can be daunting. For example, integrating email forwarding, custom URLs, and supporting multiple inboxes requires not just understanding the vCard format, but also knowing how to manage domain configurations, including DNS, email forwarding rules, and server-side handling. It is best to consult with a proffesional to configure your services and or carfully read the documentation of your domain provider.
Questions and Answers
How to use a photograph with a vCard QRCode.
Using photos within a QRCode is a difficult, but possible task. Current QRCodes have only limited space, and I can’t imagine camera getting good enough to see must QRCodes formats that encode much more data. But you never know.
QR codes can only contain 7,089 numeric characters, 4,296 alphanumeric characters, or 2,953 bytes of data, depending on the encoding type
The limited data capacity of current QR Code standards makes it difficult to embed images that are both compact and visually impressive. Your best option is to include only a single color—such as a 1x1 pixel image—which can be represented in under 0.1 KB. Due to these constraints, any image embedded directly into a QR Code as data bytes should ideally be smaller than 1 KB.
Encoding an image as raw data within a QR Code offers a key advantage: it eliminates the need for client applications to make a separate network request to retrieve the image. This is important because, although the vCard format technically supports referencing external images via URLs, major platforms like Apple and Google do not currently support this feature. As a result, including a simple image URL in your vCard is ineffective—there’s no guarantee the image will be displayed.
The ability to include image data directly in the vCard is more of a workaround than an intended feature. The vCard format is poorly suited for embedding large, non-textual data like images, especially within the tight space constraints of a QR Code. It uses a format that literally increases the size by %33.
Still, there’s reason for optimism. The capability for client applications to support external image loading is clearly possible, and there are alternative methods for encoding image-like representations in plain text. We can only hope that vendors begin to embrace more open standards instead of relying solely on proprietary implementations.
Conclusion
While vCard properties like FN, TEL, and ADR are simple and intuitive, others like EMAIL and URL can quickly become complex due to the interaction with domain name systems and various standards. Understanding how domain records interact with vCard fields enables the use of advanced features but also introduces challenges for users unfamiliar with these systems.
Learn more:
- Email forwarding with a Squarespace domain - Receive emails to a custom email address that matches your domain.
- What is a Domain Name? - Domain names are a key part of the Internet infrastructure. They provide a human-readable address for any web server available on the Internet.
- Hyperlink security - Learn hyperlink security practices.
- Google - Set up Default routing for your organization - As a Google Workspace admin, use the Default routing to set up how incoming email from internal and external senders is delivered for your organization. With default routing, you specify recipient addresses and then specify the actions to take on messages intended for those recipients.
Implementing the distribution of a vCard
Create and download a compatible vCard
Using an online virtual business card builder like Snowdon Dev vCard Generator you can create new vCard(s). Then, simply download the file and share it with your customers. We offer many custom templates and prebuilt functions, which makes our completely free vcard creator the best and easiest to use.
Share QR Codes for Efficient vCard Distribution
QR (Quick Response) codes can be effectively utilized to distribute vCards in a convenient and contactless manner. By incorporating a QR code that contains your vCard information on your business materials, such as business cards, brochures, in shop, or marketing materials, you can streamline the process of exchanging contact details. When individuals scan the QR code using their smartphones, they can instantly receive and save your vCard details without the need for manual entry.
QR codes can be displayed on web pages or printed off, making them versatile for various marketing and networking strategies. Whether incorporated into digital content or printed materials like posters and flyers, QR codes offer a flexible solution for distributing vCards across different platforms. This adaptability ensures that recipients can easily access your vCard information regardless of the medium, further enhancing the convenience and accessibility of exchanging contact details.
Additionally, at events or conferences, including a QR code on your name badge or on promotional materials enables swift and efficient sharing of your vCard with other attendees. This seamless process not only enhances networking opportunities but also reflects a modern and tech-savvy approach to exchanging contact information.
vCard QR Code from static data
To create a QR code that opens a vCard, simply generate a QR code from the file contents of a vCard. Ensure that the file is loaded appropriately or use tools to validate and correct any encoding issues. This process guarantees that the QR code correctly prduces an identical vCard, allowing recipients to instantly access and save your contact details with ease.
When creating a vCard for your QRCodes, be sure to remove any large photos, as the file sizes quickly exceed the limit of data within common QRCode protocols. It is possible but requires your graphics assets to be very small, in formats like GIF. You can learn more on creating small images here.
Using the free online tool like the Snowdon Dev vCard Generator you can export your vCard directly to a QR Code. Simply open the dialog in the View menu after entering your vCard.
How to find the QRCode viewer within our vCard Generator.
- Developers can generate qrcodes programmatically.
By following this method, you can ensure seamless integration of vCard information with QR technology, optimizing the convenience and functionality of exchanging contact information.
vCard QR Code from URL
QR codes can also link to a URL, this means that you can utilise both methods, distributing a URL to a vCard via QR codes. By only encoding the URL in the QR code, this reduces the amount of data without reducing any functionality. It also allows you to update your vCard without changing the QR code printouts.
Digital file exchange
There are multiple ways to send vcards in the applications we use. Via, a link on a website or email.
Optons One: Send the file
Add the vcf file to an email. It can be opened as a file. However, this means that the file must be resent to each email. The file size is quite small, so that is acceptable.
Options Two: Making the file available as a download
By uploading a file to a publicly exposed web server, users can download the file from the link. This gives the owner the ability to capture any downloads as events to be used in some form of analytics. It also allows you to include only a link to the file, which will yield a short string of text that refers to a larger data blob that’s automatically downloaded by the device’s applications. This reduces the number of bytes sent per email.
Once the file has been uploaded to a web server, users can instantly download your file. You can optionally also specify some headers that tell the client application that what you are sending is a file of a particular format and its filename.
On an individual file level (using Express JS):
res.set('Content-Type', 'text/vcard; name="mycontactfile.vcf"');
res.set('Content-Disposition', 'inline; filename="mycontact.vcf"');
On an entire set of file (using firebase):
{
...
"headers": [ {
"source": "vcf/**/*.@(vcf)",
"headers": [
{
"key": "Content-Type",
"value": "text/vcard; name=\"mycontactfile.vcf\""
},
{
"key": "Content-Disposition",
"value": "inline; filename=\"mycontact.vcf\""
}
]
} ]
}
Then, simply link to the file using an anchor tag.
<a href="https://mywebserver.com/vcf/mycontact.vcf">Download my contact file</a>
Or using your client (email application etc), add a hyperlink to the following URL:
https://mywebserver.com/vcf/mycontact.vcf
Conclusion
Virtual business cards are a powerful tool in the digital age, offering convenience, professionalism, and advanced features that traditional business cards cannot match. By integrating vCards into your business strategy, you can enhance your networking efforts, streamline operations, and project a modern, eco-friendly image. Embrace the future of business communication with vCards and watch your professional relationships and business opportunities flourish.
Frequently asked questions
How to open a vCard (.vcf, .vcard) file?
When you open a vCard file, you can click on it to open it in the default application, or select it in the file Explorer or another program. One common issue with vCard files is that computers may change newline characters, causing potential data corruption. To avoid this, it’s best not to edit the file’s text. Some applications not designed for vCard files may also cause encoding changes when loading and saving the file. Typically, opening a .vcf file will open it directly in the correct application, such as a contact or address book, without the need for text editing.
Why Some vCard Properties Like REV, UID, and Source May Not Work on Some Devices
The vCard properties like REV, UID, and Source are optimistic properties that enable applications to manage and identify virtual business cards. While it’s true that not all devices may fully support these properties, they play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and consistency of vCard information across different platforms. The REV property, for example, allows for version control, ensuring that old information is correctly reflected across devices when encountering a existing card. Similarly, the UID property helps in uniquely identifying and associating vCards to an idenity, enabling efficient management of contacts. While it’s unfortunate that not all devices fully support these properties, their presence is vital for interoperability and seamless management of virtual business cards.
How to Export a vCard to CSV
vCard (VCF) files are commonly used to store and share contact information between different devices and applications. While vCards are widely supported, CSV (Comma Separated Values) files are often preferred for importing contact information into spreadsheets or databases. To convert a vCard to a CSV file, follow these steps:
1. Using Online Converters
One of the easiest ways to convert a vCard file to CSV is by using online tools. These tools are quick and convenient, but keep in mind that they may have file size limitations or privacy concerns if you’re dealing with sensitive data. Here’s how to do it:
- Step 1: Search for a reputable online converter such as vCard to CSV.
- Step 2: Upload your vCard file (usually with a .vcf extension) to the website.
- Step 3: Select CSV as the output format and click “Convert” or similar.
- Step 4: Download the CSV file once the conversion is complete.
snowdon.dev vcard to csv converter
First open the snowdon.dev vCard Generator application, then open the export function File > Export. Second, select a target, for example using the file explorer.
Open the files you want to convert and click export. You can configure the settings to adjust how the output within the interface.
The free snowdon.dev vCard generator application by default does not share personal information from your vCards with our servers. All processing takes place on-device.
The snowdon.dev vcard/vcf/contact to csv converter.
12 - Doc Signing: Make E-Signing Simple, Secure, and Free
In today’s fast-paced business environment, getting documents signed quickly is essential. Whether it’s contracts, NDAs, proposals, or onboarding forms, delays in signatures can stall deals, impact cash flow, and kill momentum.
But here’s the truth: most electronic signature platforms are overpriced or overly complex. If you’re tired of clunky interfaces, per-user pricing, or monthly subscription traps—it’s time to meet DocuSeal.
What Is DocuSeal?
DocuSeal is an open-source, self-hosted e-signature platform that lets you prepare, send, and sign documents online—easily and securely. It’s perfect for small businesses, agencies, freelancers, or any team that wants full control without sacrificing convenience.
⚙️ Key Features
- 🖋 Drag-and-Drop Document Editor – Upload PDFs and add signature, text, and checkbox fields in seconds.
- 🔐 Legally Binding Signatures – Compliant with eIDAS, ESIGN, and UETA regulations.
- 💼 Reusable Templates – Save time by creating templates for commonly used forms and contracts.
- 🧑 Multi-Party Signing – Get documents signed by multiple parties in a defined order.
- 🌍 Self-Hosted or Cloud-Based – Choose full control with open-source hosting or use the hosted version.
- 💸 No Per-Signature Fees – Ideal for teams that handle high document volumes or need predictable costs.
Why Businesses Love DocuSeal
DocuSeal stands out because it gives you enterprise-grade capabilities without locking you into a contract. Unlike most competitors that charge per user or per envelope, DocuSeal keeps it simple and flexible.
For privacy-conscious organizations or anyone handling sensitive contracts, having the option to self-host DocuSeal means your documents stay within your infrastructure—no third-party risks, no external storage.
Real Use Cases
- Startups: Speed up fundraising paperwork and employee onboarding.
- Agencies: Send out client agreements or creative briefs for instant approval.
- Legal Teams: Create secure, reusable templates for standard legal forms.
- Freelancers: Look more professional and close projects faster.
Get Started Today
Ready to move on from printing, scanning, and chasing signatures?
🔗 Try DocuSeal online 📦 Explore the open-source repo 🛠 Or self-host your own secure e-signature server
Signing documents shouldn’t be a bottleneck. With DocuSeal, it’s as easy as send, sign, done.
13 - Payment: A Smarter Way to Handle Payments
As a business owner, you probably didn’t start your company because you love paperwork. But if you’re still manually sending invoices, tracking down payments, or juggling spreadsheets, you’re wasting valuable time—and losing money in the process.
Invoices are how you get paid. And yet, so many businesses treat them as an afterthought. That delay in sending or following up can lead to late payments, awkward client conversations, and cash flow issues that ripple across your business.
So, what’s the solution?
You Need to Automate Your Invoicing Workflow
Imagine this instead:
- Every client receives a branded, professional invoice on time.
- Payment reminders are automatic and polite.
- You can see which invoices are overdue at a glance.
- You don’t pay a monthly fee just to stay organized.
That’s exactly what a tool like SolidInvoice helps you achieve.
Why Stripe Is a Smart Choice for Invoicing Automation
Stripe makes invoicing fast, simple, and scalable—whether you’re sending five invoices a month or five hundred. With Stripe Invoicing, you can create and send professional, customizable invoices in minutes. It supports automatic payment reminders, real-time tracking, and built-in payment processing, all without requiring a separate subscription. Even better, Stripe seamlessly integrates with your existing systems, so you can streamline your entire payment flow without disrupting how you do business.
Ready to stop chasing payments? Stripe helps you get paid faster—with less effort.
Why We Recommend SolidInvoice
SolidInvoice is a free, open-source invoicing and billing platform built for freelancers and small businesses who want control without complexity.
Here’s what makes it stand out:
- 🔧 Fully Self-Hosted: You own your data. Install it on your own server or cloud instance.
- 🎨 Customizable Invoices: Add your branding, logo, and styling.
- 🔁 Recurring Invoices & Quotes: Save time with templates and automation.
- 📧 Email Notifications: Clients get reminders automatically.
- 💸 Multiple Payment Options: Accept payments via Stripe, PayPal, and more.
- 🔐 Secure & Modern: Built with Symfony and Twig, following modern PHP best practices.
Whether you’re managing one client or dozens, SolidInvoice gives you a professional edge—without recurring fees or vendor lock-in.
Start Getting Paid On Time
If you’re serious about growing your business, start with how you get paid. Streamlining your invoicing isn’t just a productivity boost—it’s a strategic move for your cash flow and client experience.
SolidInvoice has multiple methods of using their software, self hosting and managed Software as a Service.
👉 Check out SolidInvoice on GitHub and start taking control of your billing today.
Check out SolidInvoice managed hosting.
Still using spreadsheets? It’s time to level up.
14 - Digital Signage: Using the Web as a Display Engine
Most people think of a website as a digital document accessed via a domain name in a web browser. While that’s true, there’s a deeper capability worth exploring: modern web browsers are highly sophisticated rendering engines. In fact, rendering is now their primary function.
This opens up creative opportunities, particularly for digital signage. Because the browser can render advanced layouts and dynamic content using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, it becomes a powerful tool for driving visual displays—not just for traditional websites, but for embedded screens, kiosks, or public information terminals.
What Makes Digital Signage Different?
At first glance, a digital sign may seem no different from a regular website. And that’s actually the point: it doesn’t have to be different. The same web technologies used to build websites can be repurposed to drive digital signs. When you render a web page in fullscreen on a dedicated screen—especially when customized with branding, schedules, or live data—you get all the flexibility of the web with the focused utility of signage.
Digital signs benefit from:
- Remote updates using standard web deployment
- Responsive layouts optimized for various screen sizes and orientations
- Dynamic content integration, such as weather, news feeds, or alerts
- Reusability, with the same content being viewed on desktop and signage without duplication
Leveraging Thin Clients
One of the most efficient ways to deploy digital signage is through thin client devices. These low-cost, low-maintenance computers (such as Raspberry Pi or other ARM-based boards) run minimal software—often just a browser in kiosk mode.
Benefits of using thin clients:
- Lower hardware costs
- Simple maintenance and fewer moving parts
- Cloud-managed or local network control
- Supports modern web standards
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Another key advantage is improved electric usage. Thin clients and small display units can be optimized for low power consumption, and many setups can run entirely on solar power, especially in outdoor or remote locations. By minimizing energy requirements, digital signage becomes a green solution for continuous visual communication.
Going Beyond Static Screens
Here are some ideas to make the most of your digital signage:
- Scheduled content: Use web APIs to rotate content based on time of day or location
- Offline fallback: Use service workers to cache pages in case of connectivity issues
- Touch interactivity: Add a layer of engagement for kiosks or wayfinding systems
- Live dashboards: Integrate with tools like Grafana, Power BI, or Google Sheets
- Theming and branding: Use CSS to change looks across multiple signs with a single config
Digital signage powered by the web offers flexibility, low cost, and sustainability. Whether you’re managing a local display or a network of signs across a campus or city, the browser is no longer just a portal to the web—it’s a canvas for experience.
